Windows
Overview
The Workspaces API is accessible via the io.workspaces object.
The Live Examples section demonstrates using the Workspaces API.
Frame
The Frame is the topmost level window which contains all Workspaces.
Frame Reference
You can retrieve a reference to a Frame instance in several ways.
Current Window Frame
To retrieve the Frame in which the current window is located, use the getMyFrame() method:
// This method will return the Frame of the current window.
// If an error is thrown, the window isn't part of a Workspace.
const frame = await io.workspaces.getMyFrame().catch(console.error);All Frames
To retrieve all Frame instances, use the getAllFrames() method:
// Getting all Frames.
const allFrames = await io.workspaces.getAllFrames();Specific Frame
To retrieve a specific Frame instance, use the getFrame() method:
// Retrieving a specific Frame.
const specificFrame = await io.workspaces.getFrame(frame => frame.id === "frame-id");Frame Bounds
Once you retrieve a Frame instance, you can manipulate its bounds by using the move() and resize() methods:
const myFrame = await io.workspaces.getMyFrame();
// Moving a Frame.
await myFrame.move({ top: 100, left: 100 });
// Resizing a Frame.
await myFrame.resize({ width: 600, height: 600 });Focusing Frames
To bring a Frame instance on focus, use the focus() method:
const frame = await io.workspaces.getFrame(frame => frame.id === "frame-id");
// Focusing a Frame.
await frame.focus();Closing Frames
To close a Frame instance, use the close() method:
const frame = await io.workspaces.getFrame(frame => frame.id === "frame-id");
// Closing a Frame.
await frame.close();⚠️ Note that the result from using this method in io.Connect Browser projects may vary depending on whether the browser will allow the close operation.
Frame Workspaces
To retrieve all Workspace objects located in a Frame instance, use the workspaces() method:
const myFrame = await io.workspaces.getMyFrame();
// Retrieving all Workspaces in a Frame.
const frameWorkspaces = await myFrame.workspaces();Empty Frame
To create an empty Frame with no Workspaces in it, use the createEmptyFrame() method. It accepts an EmptyFrameDefinition object as an argument, which you can use to specify the Frame bounds and context:
const definition = {
frameConfig: {
bounds: { left: 200, top: 200, height: 700, width: 500 }
},
context: { io: 42 }
};
const emptyFrame = await io.workspaces.createEmptyFrame(definition);⚠️ Note that you can retrieve the context passed to the empty Frame via the
onInitializationRequested()method.
The empty Frame will be opened with no Workspaces in it and will show a constant loading animation until it's initialized. To initialize an empty Frame, use the init() method. It accepts a FrameInitializationConfig object as an argument that you can use to specify a list of WorkspaceDefinition or RestoreWorkspaceDefinition objects with which to initialize the empty Frame:
const configuration = {
workspaces: [
{ name: "my-workspace", restoreOptions: { context: { io: 42 }, title: "My Workspace"} },
{ name: "my-other-workspace", restoreOptions: { context: { io: "forty-two" }, title: "My Other Workspace"} }
]
};
await emptyFrame.init(configuration);⚠️ Note that the
init()method can be invoked only once and only on an emptyFrame.
⚠️ Note that the
positionIndexproperty, used for positioning Workspaces within theFrame, is ignored by theinit()method. If you want to sort the array of Workspace Layouts when loading them in an emptyFrame, you must implement the required logic yourself. A possible solution is to store a custom property inside themetadataobject of eachLayoutobject describing a Workspace and use this property to sort the Workspaces Layouts after retrieving them from your Layout store and before initializing the emptyFrame.
To check whether a Frame is empty, use the isInitialized flag. It will return false for an empty Frame:
const isFrameInitialized = myFrame.isInitialized;Workspace
A Workspace contains one or more app windows arranged in columns, rows, or groups.
Workspace Reference
You can retrieve a reference to a Workspace instance in several ways.
Current Window Workspace
To retrieve the Workspace in which the current window is located, use the getMyWorkspace() method:
// This method will return the Workspace of the current window.
// If an error is thrown, the window isn't part of a Workspace.
const workspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace().catch(console.error);All Workspaces
To retrieve all Workspaces, use the getAllWorkspaces() method:
// Retrieving all Workspaces.
const allWorkspaces = await io.workspaces.getAllWorkspaces();Specific Workspace
To retrieve a specific Workspace, use the getWorkspace() method:
// Retrieving a specific Workspace.
const specificWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getWorkspace(workspace => workspace.id === "workspace-id");Workspace State
Workspaces are designed to be freely modified programmatically as well as by the end user via the UI. Keeping a correct reference to a modified Workspace instance is important in order for your code to be able to update the Workspace accordingly. For example, the user may have already closed a Workspace element that you want to update. To avoid such errors, you can either get a new reference to that element using the API, or you can use the refreshReference() method of a Workspace instance:
// Updating the reference to an already existing Workspace instance.
await myWorkspace.refreshReference();
// When this resolves, the `myWorkspace` object will be updated to reflect the current Workspace state.Parent Frame & Child Elements
To retrieve a reference to the Frame object containing the current Workspace, use the frame property of a Workspace instance:
const myFrame = myWorkspace.frame;To retrieve a collection of the immediate child elements of a Workspace, use the children property of a Workspace instance:
const workspaceChildren = myWorkspace.children;Restoring Workspaces
You can restore a Workspace by using the restoreWorkspace() method which is available at top level of the API. It accepts an optional RestoreWorkspaceConfig object in which you can specify a title and a context for the restored Workspace:
const restoreOptions = { title: "My Workspace" };
const workspace = await io.workspaces.restoreWorkspace("myWorkspace", restoreOptions);This method is also available on the Frame instance:
const myFrame = await io.workspaces.getMyFrame();
// You don't have to specify a Frame in which to restore the Workspace.
const workspace = await myFrame.restoreWorkspace("myWorkspace");Creating Workspaces
To create Workspaces dynamically, use the createWorkspace() method available at top level of the API and on the Frame instance. Using the createWorkspace() method, however, may often be quite inconvenient as every time you want to create a Workspace, you will have to pass an object describing a full Workspace Layout. This Layout can quickly become very complex depending on the number and arrangement of apps participating in it.
The following example demonstrates creating a Workspace by passing a WorkspaceDefinition object with only two apps arranged in a single column:
// Workspace definition.
const definition = {
// Define all Workspace elements (children).
children: [
{
type: "column",
children: [
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-one"
},
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-two"
}
]
}
],
// Confugartion for the Workspace.
config: {
title: "My Workspace"
}
};
// Creating a Workspace.
const workspace = await io.workspaces.createWorkspace(definition);⚠️ Note that if you insert an empty
Column,RoworGroupelement in a Workspace (without a window as its content), it will be visually represented in the Workspace as an empty space with a grey background and a button in the middle from which the user will be able to add an app. The user won't be able to move or close this empty element.
This method is also available on the Frame instance (instance of a Workspaces App). Using createWorkspace() from a Workspaces App instance will create the Workspace within that Workspaces App:
// Define an empty Workspace.
const definition = { children: [] };
const myFrame = await io.workspaces.getMyFrame();
const workspace = await myFrame.createWorkspace(definition);ℹ️ For more details on how to use new or existing Frames or target different Workspaces Apps when creating a Workspace, see the Targeting section.
Workspaces Builder API
An easier solution for creating Workspaces is to use the Workspaces Builder API. The builder allows you to compose entire Workspaces as well as different Workspace elements (rows, columns or groups) depending on the builder type you set.
You can define a builder with the getBuilder() method. It accepts a BuilderConfig object as a parameter in which you should specify the type of the builder ("workspace", "row", "colum" or "group") and provide either a Workspace definition or a definition for the element (row, column or group) you want to build. You can then use the methods of the builder instance to add rows, columns, groups or windows.
The following example demonstrates how to create a Workspace using a builder:
// Configuration for the builder.
const builderConfig = {
// Type of the builder.
type: "workspace",
definition: {
// Pass only the Workspace configuration without defining Workspace children.
config: {
title: "My Workspace"
}
}
};
// Access the Workspaces Builder API and define a builder.
const builder = io.workspaces.getBuilder(builderConfig);
// Use the builder methods to add a column and two windows in it.
builder
.addColumn()
.addWindow({ appName: "app-one" })
.addWindow({ appName: "app-two" });
// Finally, use the `create()` method of the builder instance to create the Workspace.
const workspace = await builder.create();Targeting
When creating or restoring a Workspace, you can target existing Frame instances, or create new ones in which to load the Workspace.
Existing Frame
To reuse an existing Frame instance when creating or restoring a Workspace, specify the ID of the Frame in the WorkspaceDefinition or the RestoreWorkspaceConfig object respectively:
const frameID = "frame-id";
// Create a Workspace in an existing Frame.
const definition = { children: [], frame: { reuseFrameId: frameID } };
await io.workspaces.createWorkspace(definition);
// Restore a Workspace in an existing Frame.
const restoreOptions = { frameId: frameID };
await io.workspaces.restoreWorkspace("myWorkspace", restoreOptions);New Frame
To open a new Frame when creating or restoring a Workspace, use the newFrame property of the WorkspaceDefinition or the RestoreWorkspaceConfig object respectively. Set the newFrame property to true or pass a NewFrameConfig object to it describing the options for the new Frame:
// Create a Workspace in a new Frame.
const definition = {
children: [],
frame: {
newFrame: {
bounds: {
top: 10,
left: 10,
height: 1000,
width: 1500
}
}
}
};
await io.workspaces.createWorkspace(definition);
// Restore a Workspace in a new Frame.
const restoreOptions = { newFrame: true };
await io.workspaces.restoreWorkspace("myWorkspace", restoreOptions);Focusing Workspaces
To specify whether a Workspace should be on focus when creating or restoring it, use the isSelected property of the WorkspaceConfig or RestoreWorkspaceConfig objects respectively:
const definition = {
children: [
{
type: "column",
children: [
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-one"
},
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-two"
}
]
}
],
config: {
title: "My Workspace",
isSelected: false
}
};
await io.workspaces.createWorkspace(definition);Positioning Workspaces
To specify a position for the Workspace when creating or restoring it, use the positionIndex property of the WorkspaceConfig or RestoreWorkspaceConfig objects respectively:
const restoreOptions = { positionIndex: 1 };
await io.workspaces.restoreWorkspace("myWorkspace", restoreOptions);⚠️ Note that the
positionIndexproperty is ignored by theinit()method for initializing an emptyFrame. If you want to sort the array of Workspace Layouts when loading them in an emptyFrame, you must implement the required logic yourself. A possible solution is to store a custom property inside themetadataobject of eachLayoutobject describing a Workspace and use this property to sort the Workspaces Layouts after retrieving them from your Layout store and before initializing the emptyFrame.
⚠️ Note that the groups of pinned and unpinned Workspaces are arranged independently of each other, so using the
positionIndexproperty of a pinned Workspace will define its position within the pinned Workspaces group.
Pinning & Unpinning Workspaces
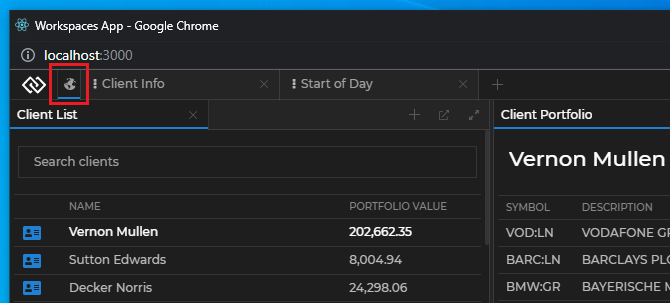
Workspaces can be pinned or unpinned programmatically in the Workspaces App. Pinned Workspace tabs are placed before the regular Workspace tabs and are represented only by their icon - they don't have a title, nor a Workspace tab menu or a "Close" button, therefore they can't be closed and their initial Layout can't be overwritten by the end user.
The following image shows a pinned Workspace with a custom icon followed by two regular unpinned Workspaces:
You must specify an icon for the Workspace in order to be able to pin it. To set an icon for a Workspace, use the icon property of the WorkspaceConfig or RestoreWorkspaceConfig objects when creating or restoring a Workspace respectively, or use the setIcon() method of a Workspace instance. The icon must be in string format and you can pass either a path to a web resource or a string representation of an image, such as Base64.
The following example demonstrates how to set an icon for a Workspace when restoring a Workspace Layout:
const restoreOptions = { icon: "https://example.com/icon.svg" };
await io.workspaces.restoreWorkspace("myWorkspace", restoreOptions);The following example demonstrates how to set an icon for a Workspace using the setIcon() method:
const icon = "https://example.com/icon.svg";
await myWorkspace.setIcon(icon);To get the icon of a Workspace, use the getIcon() method:
const icon = await myWorkspace.getIcon();To pin a Workspace, use the pin() method and optionally pass an icon. The title, the Workspace tab menu and the "Close" button of the Workspace tab will be removed and the icon of the Workspace will be shown as the last item in the pinned Workspaces group:
const options = {
icon: "https://example.com/icon.svg"
};
await myWorkspace.pin(options);To unpin a Workspace, use the unpin() method. The title, the Workspace tab menu and the "Close" button will be returned, the Workspace icon will be hidden and the Workspace will be added as the first tab in the unpinned Workspaces group:
await myWorkspace.unpin();To specify whether a Workspace should be pinned when creating or restoring it, use the isPinned property of the WorkspaceConfig or RestoreWorkspaceConfig objects respectively:
const restoreOptions = { isPinned: true };
await io.workspaces.restoreWorkspace("myWorkspace", restoreOptions);Finding Workspace Elements
The Workspaces API offers various methods for finding elements in a Workspace - Row, Column, Group and WorkspaceWindow. All methods for querying Workspaces accept a predicate function as a parameter which you can use to find the desired Workspace elements.
Box Elements
Box elements are Workspace elements that can contain other Workspace elements - Row, Column and Group. These elements are the building blocks of a Workspace Layout, while the actual windows (app instances) can be viewed as their content.
⚠️ Note that the actual app instances are described by the
WorkspaceWindowobjects and are meant to be hosted inGroupobjects. This way, theWorkspaceWindowobjects can be displayed as tabbed windows in the UI of the Workspaces App. If aWorkspaceWindowobject is placed directly inside aColumnor aRowobject, the app window will be static and without a tab - the user won't be able to move it, close it, or add other windows to it, and manipulating it will be possible only programmatically via the API.
To retrieve all box elements in a Workspace, use the getAllBoxes() method of a Workspace instance:
const myWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
// This will return all `Row`, `Column` and `Group` elements in the Workspace.
const allBoxElements = myWorkspace.getAllBoxes();The Workspace instance also offers methods for specific types of box elements. For example, to get all rows in a Workspace, use the getAllRows() method:
const myWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
const allRows = myWorkspace.getAllRows();To retrieve all columns or groups, use the getAllColumns() or getAllGroups() method respectively.
You can also retrieve a specific box element using the getBox() method available on top level of the API as well as on a Workspace instance. The following example demonstrates how to get the immediate parent element of a window using the window ID:
const myWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
// The `getBox()` method (as most methods for querying Workspaces)
// accepts a predicate function used to find the desired elements.
const targetElement = myWorkspace.getBox((boxElement) => {
return boxElement.children.some(child => child.type === "window" && child.id === "target-id");
});The Workspace instance also offers methods for finding specific rows, columns or groups - getRow(), getColumn() and getGroup().
Workspace Windows
To get all windows in a Workspace, use the getAllWindows() method of a Workspace instance:
const myWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
const allWorkspaceWindows = myWorkspace.getAllWindows();To get a specific window, use the getWindow() method available on top level of the API as well as on a Workspace instance:
const specificWindow = await io.workspaces.getWindow(window => window.id === "target-id");Editing Workspaces
Workspace instances and Box element instances offer methods for adding and removing Workspace elements. This, combined with the powerful querying methods, gives you full programmatic control over a Workspace.
The following example demonstrates how to add a new window as a sibling to another window in a Workspace using the addWindow() method of a box element:
const myWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
const targetElement = myWorkspace.getBox((boxElement) => {
return boxElement.children.some(child => child.type === "window" && child.id === "target-id");
});
await targetElement.addWindow({ appName: "app-three" });Manipulating Workspace Elements
Once you have a reference to any Box or WorkspaceWindow element, you can use its methods to manipulate its state and content.
Maximize & Restore
To maximize a Workspace element within the bounds of the Workspace, use its maximize() method:
await targetElement.maximize();To restore a Workspace element after maximizing it, use its restore() method:
await targetElement.restore();Remove Child Elements
To remove an immediate child element from any Box element, use its removeChild() method. It accepts a predicate that you can use as a filter to find the desired child element:
const predicate = child => child.id === "target-id";
await targetElement.removeChild(predicate);Close
To close any Workspace element (and all its children, if any), use its close() method:
await targetElement.close();Size Constraints
Workspace elements can have size constraints which will prevent the user from resizing them beyond the set limits. Workspace rows and columns can also be pinned, meaning that the size of the pinned element (width for columns, height for rows) will be preserved when the user maximizes, restores or resizes the Workspace.
The following table lists the available size constraint properties and the Workspace elements to which they apply:
| Property | Type | Description | Applies to |
|---|---|---|---|
isPinned |
boolean |
Specifies whether the size of the element (width for columns, height for rows) will be preserved when the user maximizes, restores or resizes the Workspace. | Row, Column |
maxHeight |
number |
Sets the maximum height in pixels of the element. | Row, Group, Window |
maxWidth |
number |
Sets the maximum width in pixels of the element. | Column, Group, Window |
minHeight |
number |
Sets the minimum height in pixels of the element. | Row, Group, Window |
minWidth |
number |
Sets the minimum width in pixels of the element. | Column, Group, Window |
Mind that if you set the same max or min property of more than one of several nested elements to different values (e.g., you've set maxWidth: 400 for a column and maxWidth: 500 for a window inside that column), then in the case of maximum values, the lower one will be used, and in the case of minimum values, the higher one will be used. This way, all defined constraints will be respected when the user resizes the Workspace or its elements.
To set size constraints for Workspace elements when creating a Workspace, use the config property of the WorkspaceDefinition object:
const definition = {
children: [
{
type: "column",
children: [
{
type: "group",
children: [
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-two"
}
],
},
{
type: "group",
children: [
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-two",
config: {
// Window size constraints.
maxWidth: 500,
minHeight: 200
}
}
],
}
],
config: {
// The column will be constrained to 400 px width.
// The maximum width of the column will override the one of the window
// because it's set to a lower value.
maxWidth: 400
}
}],
config: {
title: "My Workspace"
}
};
const workspace = await io.workspaces.createWorkspace(definition);⚠️ Note that if the specified constraints are invalid, they will be ignored - e.g., when min exceeds max or conflicting constraints between different elements.
You can set size constraints also when using the Workspaces Builder API or when adding Workspace elements using the addRow(), addColumn(), addGroup() or addWindow() methods of a Workspace instance or box elements:
const rowDefinition = {
type: "row",
children: [
{
type: "group",
children: [
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-two"
}
],
}
],
config: {
// The row will be pinned - its height will be preserved when the user resizes the Workspace.
isPinned: true
}
};
await myWorkspace.addRow(rowDefinition);Hibernation
To hibernate a Workspace instance, use the hibernate() method of a Workspace instance:
const myWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
await myWorkspace.hibernate();To resume a hibernated Workspace, use the resume() method of a Workspace instance:
const myWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
await myWorkspace.resume();ℹ️ For more details on how to configure Workspace hibernation, see Hibernation in the Enabling Workspaces section.
Loading Strategies
To specify a loading strategy for a Workspace when creating it, use the loadingStrategy property of the config object in the WorkspaceDefinition object:
const definition = {
config: {
loadingStrategy: "lazy"
}
};
const workspace = await io.workspaces.createWorkspace(definition);To specify a loading strategy for a Workspace when restoring it, use the loadingStrategy property of the RestoreWorkspaceConfig object:
const options = { loadingStrategy: "lazy" };
const workspace = await io.workspaces.restoreWorkspace("My Workspace", options);ℹ️ For more details on how to to provide settings for Workspace loading strategies, see the Enabling Workspaces > Main App > Loading Strategies section.
Lock Settings
Workspace instances, Group, Row, Column and WorkspaceWindow elements can be locked using the lock() method of the respective instance. Locking a Workspace or any of its elements allows you to control the extent to which the user can modify it. For instance, you may want to prevent the user from removing or extracting a window from the Workspace, but at the same time allow them to resize the Workspace contents, or you may want to disable any Workspace modifications whatsoever.
The lock() method accepts as an optional argument either a WorkspaceLockConfig object or a callback that will receive the current WorkspaceLockConfig as an argument and must return an object. If you don't provide a locking configuration, all locking properties (applicable to the respective element) will be automatically set to false:
const myWorkspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
// Will set all Workspace locking properties to `false`.
await myWorkspace.lock();The following example demonstrates how to lock only specific properties:
const lockConfig = { allowDrop: false };
await myWorkspace.lock(lockConfig);
// Or
const setLocking = (lockConfig) => {
lockConfig.allowDrop = false;
return lockConfig;
};
await myWorkspace.lock(setLocking);⚠️ Note that passing a callback instead of an object with locking config to the
lock()method is a more future proof approach because if new locking properties are introduced in the future, your app behavior won't be affected.
To set all locking properties to true, pass an empty object as an argument:
myWorkspace.lock({});Locking properties for a Workspace:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowDropBottom |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the bottommost area of the Workspace. |
allowDropLeft |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the leftmost area of the Workspace. |
allowDropRight |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the rightmost area of the Workspace. |
allowDropTop |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the topmost area of the Workspace. |
allowExtract |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from extracting (or rearranging) windows inside the Workspace. |
allowSplitters |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the splitters from being draggable, so the Workspace elements can't be resized . |
showAddWindowButtons |
boolean |
If false, will hide all "Add Window" buttons (the "+" buttons) in the headers of window groups. |
showCloseButton |
boolean |
If false, will hide the "Close" button in the Workspace tab. |
showEjectButtons |
boolean |
If false, will hide all "Eject" buttons in the headers of window groups. |
showSaveButton |
boolean |
If false, will hide the "Save" button in the Workspace tab. |
showWindowCloseButtons |
boolean |
If false, will hide all "Close" buttons in the window tabs. |
Locking properties for a Group:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowDropBottom |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the bottommost area of the window group. |
allowDropHeader |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the header area of the window group. |
allowDropLeft |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the leftmost area of the window group. |
allowDropRight |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the rightmost area of the window group. |
allowDropTop |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from dropping windows in the topmost area of the window group. |
allowExtract |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from extracting windows from the window group. |
allowReorder |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from reordering the windows in the window group. |
showAddWindowButton |
boolean |
If false, will hide the "Add Window" button (the "+" button) in the header of the window group. |
showEjectButton |
boolean |
If false, will hide the "Eject" button in the header of the window group. |
showMaximizeButton |
boolean |
If false, will hide the "Maximize" button in the header of the window group. |
Locking properties for a Row:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowSplitters |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the splitters from being draggable, so the Workspace row can't be resized . |
Locking properties for a Column:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowSplitters |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the splitters from being draggable, so the Workspace column can't be resized . |
Locking properties for a WorkspaceWindow:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
allowExtract |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from extracting the window from the Workspace. |
allowReorder |
boolean |
If false, will prevent the user from reordering the window in the window group. |
showCloseButton |
boolean |
If false, will hide the "Close" button on the window tab. |
To set the locking properties of a Workspace and any of its elements when creating it, use the config property of the WorkspaceDefinition object. The locking configuration of a Workspace element will override the locking configuration of the Workspace:
const definition = {
children: [
{
type: "column",
children: [
{
type: "group",
children: [
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-two"
}
],
},
{
type: "group",
children: [
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-two",
config: {
// This will override the Workspace locking config.
allowExtract: true,
showCloseButton: true
}
}
],
}
]
}],
config: {
title: "My Workspace",
// Workspace locking config.
allowExtract: false,
showSaveButton: false,
showCloseButton: false,
allowSplitters: false,
showEjectButtons: false,
showAddWindowButtons: false,
showWindowCloseButtons: false
}
};
const workspace = await io.workspaces.createWorkspace(definition);You can set locking configuration for a Workspace and its elements also when using the Workspaces Builder API or when adding Workspace elements using the addRow(), addColumn(), addGroup() or addWindow() methods of a Workspace instance or box elements:
const rowDefinition = {
type: "row",
children: [
{
type: "group",
children: [
{
type: "window",
appName: "app-two"
}
],
}
],
config: {
allowDrop: false
}
};
await myWorkspace.addRow(rowDefinition);Workspace Layouts
Workspace Layouts are objects that describe the content and arrangement of a Workspace. Workspace Layouts can be saved locally or remotely, deleted, exported, and imported.
The Workspaces Layouts API is accessible via the io.workspaces.layouts object.
Workspace Layout Summaries
To retrieve the WorkspaceLayoutSummary objects for all Workspace Layouts without the extensive data describing their structure, use the getSummaries() method:
const layoutSummaries = await io.workspaces.layouts.getSummaries();
// E.g., you may need only the names of the Workspace Layouts.
const allLayoutNames = layoutSummaries.map(summary => summary.name);Saving Workspace Layouts
To save the Layout of a Workspace after creating it, use the saveLayout() method of a Workspace instance:
// Saving the Layout of a previously created Workspace instance.
await workspace.saveLayout("my-workspace");To save the Layout of any opened Workspace, use the save() method of the Workspaces Layouts API and pass a WorkspaceLayoutSaveConfig object as a required argument:
// It's required to specify the name and the ID of the Workspace.
const config = {
name: "my-workspace",
workspaceId: "workspace-id"
};
await io.workspaces.layouts.save(config);Deleting Workspace Layouts
To delete a Workspace Layout, use the delete() method of the Workspaces Layouts API and pass the name of the Workspace to delete as a required argument:
await io.workspaces.layouts.delete("workspace-one");Workspace Context
Each Workspace instance has a dedicated context (based on Shared Contexts). Use the Workspace context to pass custom data to the Workspace apps when creating or restoring a Workspace.
Initial
To specify initial context data when creating a Workspace, use the context property of the WorkspaceDefinition object:
const definition = {
context: { clientID: 1 }
};
const workspace = await io.workspaces.createWorkspace(definition);To specify initial context data when restoring a Workspace, use the context property of the RestoreWorkspaceConfig object:
const restoreOptions = {
context: { clientID: 1 }
};
const workspace = await io.workspaces.restoreWorkspace("myWorkspace", restoreOptions);Get
To get the Workspace context, use the getContext() method of a Workspace instance:
const context = await myWorkspace.getContext();Set
To set the Workspace context, use the setContext() method of a Workspace instance. Using this method will overwrite entirely the existing context:
const newContext = { instrument: "MSFT" };
await myWorkspace.setContext(newContext);Update
To update the Workspace context, use the updateContext() method of a Workspace instance. Using this method will merge the update with the existing context:
// Existing context: `{ clientID: 1 }`.
const update = { instrument: "MSFT" };
await myWorkspace.updateContext(update);
// Result: `{ clientID: 1, instrument: "MSFT" }`.Events
The Workspaces API exposes events at different levels allowing you to listen only for the events you are interested in.
Global Events
Global events are accessible at top level of the API. The following example demonstrates how to handle an event which will fire every time a window has been added to any Workspace in any Frame:
io.workspaces.onWindowAdded((window) => {
console.log(`Window added: ${window.id}`);
});All event methods return an unsubscribe function which you can use to stop receiving notifications about the event:
const unsubscribe = await io.workspaces.onWindowAdded((window) => {
console.log(`Window added: ${window.id}`);
});
unsubscribe();ℹ️ For more available global events, see the Workspaces API Reference Documentation.
Frame Events
The Frame events provide notifications when a certain action has occurred within the Frame. The following example demonstrates how to handle an event which will fire every time a window has been added to the specified Frame instance:
const myFrame = await io.workspaces.getMyFrame();
myFrame.onWindowAdded((window) => {
console.log(`Window added to Frame: ${window.id}`);
});ℹ️ For more available Frame events, see the Workspaces API Reference Documentation.
Workspace Events
The Workspace events provide notifications when a certain action has occurred within the Workspace. The following example demonstrates how to handle an event which will fire every time a window has been added to the specified Workspace instance:
const workspace = await io.workspaces.getMyWorkspace();
workspace.onWindowAdded((window) => {
console.log(`Window added to Workspace: ${window.id}`);
});ℹ️ For more available Workspace events, see the Workspaces API Reference Documentation.
Window Events
The window level events provide notifications when a certain action related to the window has occurred. The following example demonstrates how to handle an event which will fire when the window has been removed from the Workspace:
const workspaceWindow = await io.workspaces.getWindow(window => window.id === "my-window-id");
workspaceWindow.onRemoved((window) => {
console.log(`Window removed from Workspace: ${window.id}`);
});ℹ️ For more available window events, see the Workspaces API Reference Documentation.
Live Examples
Restoring and Closing Workspaces
The following app demonstrates how to restore and close programmatically already defined Workspace Layouts. Click the "Open" button of either of the two defined Workspaces to open an instance of it. The app will log the ID of the newly opened instance and provide a "Close" button for closing this particular Workspace instance. You can also define a custom context which the restored Workspace will pass to all apps participating in it. You can manipulate freely the restored Workspaces, as in the previous example.
ℹ️ Keep in mind that if you create and save a new Workspace, you will have to refresh the app to see the newly saved Workspace Layout. If you close a restored Workspace directly from its frame and then try to close it from the "Close" button for its instance, the app will show an error that this Workspace has already been closed.
Manipulating Workspaces
The app above opens a fully functioning Workspace. There are multiple registered apps which you can use to customize the Workspace Layout. You can:
- drag and drop the already opened apps to form new rows, columns or window groups;
- maximize and restore a window or window group;
- eject a window from a Workspace;
- reorder the window and Workspace tabs;
- add new app instances to the current Workspace (in the current column, row or group);
- resize the windows in the Workspace by dragging their borders;
- close and restore a Workspace within the same Frame;
- create a new Workspace, customize its Layout and save it;
API Reference
For a complete list of the available Workspaces API methods and properties, see the Workspaces API Reference Documentation.
