Data Sharing Between Apps
Overview
In certain workflow scenarios, your app may need to start (or activate) a specific app. For instance, you may have an app showing client portfolios with financial instruments. When the user clicks on an instrument, you want to start an app which shows a chart for that instrument. In other cases, you may want to present the user with several options for executing an action or handling data from the current app.
The Intents API makes all that possible by enabling apps to register, find, and raise Intents.
⚠️ Note that the following sections describe the standalone io.Connect Intents API which, while providing full support for working with FDC3 Intents and contexts, is designed to be used entirely independently of the FDC3 standard. Unlike the FDC3 Intents API, the io.Connect Intents API doesn't impose restrictions on Intent and context naming. This means that in the context of the io.Connect framework, there are no "standard" or "custom" Intents, which allows for complete freedom and flexibility when using Intents. The io.Connect Intents API supports all functionalities described in the FDC3 standard and provides a rich set of additional features.
The case with the "Portfolio" and the "Chart" app above can be implemented in the following way:
The "Chart" app registers an Intent called "ViewChart", specifying the data type (predefined data structure) that it works with - e.g., "Instrument".
When the user clicks on on instrument, the "Portfolio" app raises the "ViewChart" Intent, optionally specifying an Intent target, data type and app start up options.
This way, the "Portfolio" and "Chart" apps can be completely decoupled. If later the "Chart" app needs to be replaced, the new app for showing charts only needs to register the same Intent in order to replace the old one (provided that it works with the "Instrument" data structure as well).
Another case where the Intents API can be useful is if you want to find (and possibly filter) all apps that have registered a certain Intent. This may be because you want to present the user with all available (or appropriate) options for executing an action or handling data - e.g., on hover over an instrument or when clicking an instrument, the user sees a menu with all apps that have registered the Intent "ViewChart" and can work with the "Instrument" data structure:
All apps that can visualize data in charts register an Intent called "ViewChart", specifying the data structure they work with. Some of them work with "Instrument" data type, others work with different data types.
When the user clicks on an instrument in the "Portfolio" app, the "Portfolio" app searches for all registered Intents with a name "ViewChart" and filters them by the data type they work with.
The user sees a menu built on the fly which shows all currently available apps for visualizing charts that work with "Instrument" data type.
Defining Intents
Intents can be defined via the app definition by using the intents top-level key and can also be registered dynamically.
It's possible for different apps to register an Intent with the same name, which is useful when several apps perform the same action or work with the same data structure. This allows for easy replacement of apps. You may have an old app that has registered an Intent called "ViewChart" which you want to replace with a new app. Your new app only needs to register the same Intent (you can either remove the old app or leave it as an additional option for the users who prefer it). No changes to the calling app are necessary - when it raises the "ViewChart" Intent, the new app will be called.
To define an Intent, use the intents top-level key in the app definition:
import IOBrowserPlatform from "@interopio/browser-platform";
const config = {
licenseKey: "my-license-key",
applications: {
local: [
{
name: "Instrument Chart",
details: {
url: "http://localhost:4242/chart"
},
// Intent definitions.
intents: [
{
name: "ViewChart",
displayName: "Instrument Chart",
contexts: ["Instrument"]
}
]
}
]
}
};
const { io } = await IOBrowserPlatform(config);| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
contexts |
string[] |
The type of predefined data structures with which the app can work. |
displayName |
string |
The display name of the Intent. Can be used in context menus, etc., to visualize the Intent. |
name |
string |
Required. The name of the Intent. |
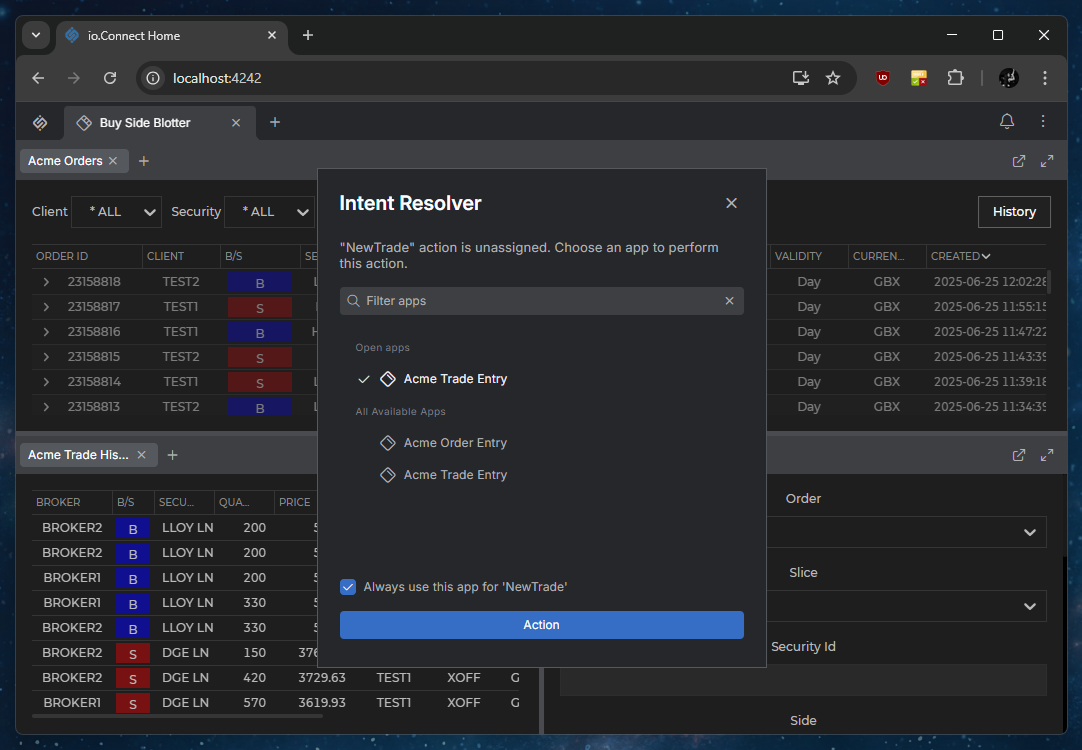
Intent Resolver
The @interopio/intent-resolver-ui library allows you to use the io.Connect Intent Resolver UI in your io.Connect Browser apps.
The Intent Resolver UI enables users to manually select which app to handle the raised Intent and to choose whether to start a new instance of an Intent handler or use an already running instance of it:
Available since io.Connect Browser 4.0
To use the io.Connect Intent Resolver UI in your io.Connect Browser project, you must:
Configure the Intent Resolver in the Main app - provide URLs pointing to the locations of the bundle, styles, and fonts for the Intent Resolver, block any origins from using the Intent Resolver. You can use the default bundles, styles, and fonts provided by the
@interopio/intent-resolver-uilibrary.Explicitly enable or disable using the Intent Resolver in the configuration object for the internal initialization of the
@interopio/browserlibrary.Explicitly enable or disable using the Intent Resolver in the configuration object for initializing the
@interopio/browserlibrary in your Browser Client apps.
Main App
To configure the Intent Resolver in the Main app, use the intentResolver property in the configuration object for initializing the Main app.
The following example demonstrates configuring the Intent Resolver in the Main app:
import IOBrowserPlatform from "@interopio/browser-platform"
const config = {
licenseKey: "my-license-key",
// Settings for the Intent Resolver.
intentResolver: {
sources: {
// It's required to specify the locations of the bundle and styles for the Intent Resolver.
bundle: "https://my-intent-resolver/intent-resolver-bundle.js",
styles: ["https://my-intent-resolver/styles.css", "https://example.com/custom-styles.css"],
// It's required to specify the locations of the fonts when using the default Intent Resolver.
fonts: ["https://my-intent-resolver/fonts.css"]
}
},
browser: {
// Enabling the Main app to use the Intent Resolver.
intentResolver: {
enable: true
}
}
};
const { io } = await IOBrowserPlatform(config);The intentResolver object has the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
blockList |
string[] |
List of origins to block from using the Intent Resolver (e.g., ["https://example.com/*"]). |
sources |
object |
Required. Use to specify the locations of the bundle, styles, and fonts for the Intent Resolver. |
The sources object has the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
bundle |
string |
Required. URL pointing to the location of the Intent Resolver bundle. The bundle must be hosted in order for Browser Client apps to be able to use it. If you provide it as a static resource, only the Main app will be able to use it. |
fonts |
string[] |
List of URLs pointing to the locations of the Intent Resolver fonts. |
styles |
string[] |
Required. List of URLs pointing to the locations of the Intent Resolver styles. |
Browser Clients
To enable the Intent Resolver for a Browser Client app, use the intentResolver property of the optional configuration object for initializing the @interopio/browser library.
The following example demonstrates configuring the Intent Resolver in a Browser Client app:
import IOBrowser from "@interopio/browser";
const options = {
intentResolver: {
// Enabling the Intent Resolver for the current Browser Client app.
// It's required to specify this to be able to use the Intent Resolver.
enable: true
}
};
const io = await IOBrowser(options);The intentResolver object has the following properties:
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
awaitFactory |
boolean |
If true (default), the @interopio/browser library will wait for the IOBrowserIntentResolverUI() factory function to resolve before completing its initialization. |
enable |
boolean |
Required. If true, will enable the Intent Resolver for the Browser Client unless the app origin has been blocked in the Main app configuration. |
timeout |
number |
Interval in milliseconds to wait for the IOBrowserIntentResolverUI() factory function to be fetched from the remote source. Defaults to 5000. |
Extending the Intent Resolver
To use your own custom Intent Resolver, provide it as a React component to the @interopio/intent-resolver-ui library by extending its configuration.
The @interopio/intent-resolver-ui library enables you to provide your own custom Intent Resolver app as a React component. By default, your component will receive as props the initialized io.Connect API object (io) and a config object describing the raised Intent.
ℹ️ For more details on the default props received by the component, see the
IntentResolverPropsinterface in theintent.resolver.ui.d.tsfile distributed with the library.
After implementing your custom Intent Resolver component, you must extend the configuration of the IOBrowserIntentResolverUI() factory function. Use the customIntentResolver property of the configuration object for initializing the @interopio/intent-resolver-ui library to provide your custom Intent Resolver component:
import IOBrowserIntentResolverUI from "@interopio/intent-resolver-ui";
import { MyCustomIntentResolver } from "./MyCustomIntentResolver";
// Define your custom factory function that accepts the initialized io.Connect API object
// and a configuration object for the `@interopio/intent-resolver-ui` library.
const MyCustomIntentResolverFactory = (io, config) => {
const extendedConfig = {
...config,
// Provide your custom Intent Resolver component.
customIntentResolver: MyCustomIntentResolver
};
// Return the invocation of the default factory function with the extended configuration.
return IOBrowserIntentResolverUI(io, extendedConfig);
};
if (typeof window !== "undefined") {
// Inject your custom factory function in the global `window` object as `IOBrowserIntentResolverUI`.
window.IOBrowserIntentResolverUI = MyCustomIntentResolverFactory;
};
export default MyCustomIntentResolverFactory;Styles
Available since io.Connect Browser 4.1
To customize the styles of the Intent Resolver, use the CSS variables provided by the io.Connect themes.
